Difference between revisions of "SQL Indexing"
From Suhrid.net Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
[[File:index-leaf-nodes.jpg|frameless|500px|From :http://use-the-index-luke.com]] | [[File:index-leaf-nodes.jpg|frameless|500px|From :http://use-the-index-luke.com]] | ||
* The Index Leaf nodes however are stored in an arbitrary order on the disk - not according to logical order. Therefore the DB needs a second data structure to find the index leaf nodes quickly. | * The Index Leaf nodes however are stored in an arbitrary order on the disk - not according to logical order. Therefore the DB needs a second data structure to find the index leaf nodes quickly. | ||
| − | * This is the Balanced Tree : B-Tree. The | + | * This is the Balanced Tree : B-Tree. The branch nodes store the max value of the index leaf node. The root node in turn points to the branch node. |
| − | + | * Traversing a B-Tree is efficient. Tree depth grows logarithmically compared to the number of indexes. | |
| − | http://use-the-index-luke.com | + | [[File:btree-index.jpg|frameless|500px|From :http://use-the-index-luke.com]] |
Revision as of 07:01, 2 October 2014
These are notes that I took about SQL Indexing from http://use-the-index-luke.com
Introduction
- An index makes a SQL query fast.
- An index is a distinct structure in the DB that requires its own space.
- A DB index is similar to index of a book - key concept is all entries are arranged in a well-defined order. Finding data in an ordered set is fast and easy because the sort order determines each entries position.
- A DB index however undergoes constant change. Whenever INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE's are executed, the index must also be updated without moving around large amounts of data.
- The DB combines two data structures for providing indexing - doubly linked lists and search trees.
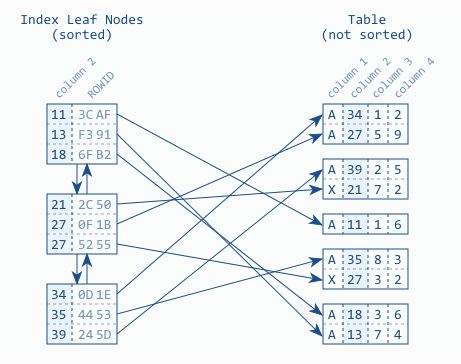
- Doubly linked list enables DB to read indexes forwards and backwards. Index leaf nodes store the indexes in a DB block or page. The blocks are logically stored in the doubly linked list.
- The Index Leaf nodes however are stored in an arbitrary order on the disk - not according to logical order. Therefore the DB needs a second data structure to find the index leaf nodes quickly.
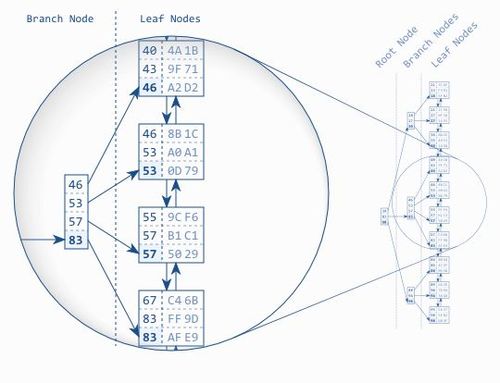
- This is the Balanced Tree : B-Tree. The branch nodes store the max value of the index leaf node. The root node in turn points to the branch node.
- Traversing a B-Tree is efficient. Tree depth grows logarithmically compared to the number of indexes.