Difference between revisions of "Model Driven Engineering"
From Suhrid.net Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
* For e.g UML2 Tools is a set of GMF-based editors for viewing and editing UML models. | * For e.g UML2 Tools is a set of GMF-based editors for viewing and editing UML models. | ||
* GMF Tooling Workflow: | * GMF Tooling Workflow: | ||
| − | + | http://wiki.eclipse.org/images/5/59/Overview.png | |
= Epsilon = | = Epsilon = | ||
Revision as of 05:28, 9 June 2012
- All forms of engineering rely on models as essential to understanding complex real-world systems.
- The basic ideas of models, modeling, and model transformation are the basis for a set of software development approaches that are known as model-driven development (MDD).
- OMG champions a style of MDD called Model-Driven Architecture (MDA). It is based on a set of emerging standards for how to define a set of models, notations, and transformation rules.
- The MDA approach provides an open, vendor-neutral basis for system interoperability via OMG’s established modeling standards: Unified Modeling Language (UML), Meta-Object Facility (MOF), and Common Warehouse Metamodel (CWM). Platformindependent descriptions of enterprise solutions can be built using these modeling standards.
- By thinking of software and system development as a set of model refinements, the transformations between models become first-class elements of the development process.
- The ability to analyze, automate, and transform models requires a clear, unambiguous way to describe the semantics of the models. Hence, the models intrinsic to a modeling approach must themselves be described in a model, which we call a metamodel.
- OMG defined a set of metamodeling levels, and defined a standard language for expressing metamodels, the Meta-Object Facility (MOF). A metamodel uses MOF to formally define the abstract
syntax of a set of modeling constructs.
Contents
Eclipse Modeling
Eclipse Modeling Framework (EMF)
- EMF is a modeling framework and code generation facility for building tools and other applications based on a structured data model.
- From a model specification described in XMI, EMF provides tools and runtime support to produce a set of Java classes for the model, along with a set of adapter classes that enable viewing and command-based editing of the model, and a basic editor.
- A domain model represents that data we want to work with. The data should be modeled irrespective of the application logic.
- Eclipse EMF is used to model these domain models.EMF makes a distinction between Meta models and actual model. The meta model describes the structure of the model and the model with data is an instance of this meta model.
- In the UML world, this is equivalent to a class diagram which describes the meta-model and an object digram describes the actual model.
- EMF provides a pluggable framework to store the model definition, the default method is to use XMI.
- The Meta model can be specified in different ways - XMI, Java annotations, UML/XML schema, textual syntax called EMFatic, Graphical editors within EMF.
- EMF has two meta models. ECore and Genmodel.
- The Ecore metamodel contains the information about the defined classes. The Genmodel contains additional information for generating code, e.g. the path and file information. The genmodel contains also the control parameter how the coding should be generated.
- The Ecore model allows the definition of the following elements:
- EClass
- EAttribute
- EReference: One end of an association between two classes.
- EDataType: Type of an attribute.
- Ecore model editor shows the model itself as the root, followed by the packages, then classes and then attributes.
- UML2 modeling is an EMF-based implementation of the UML 2.x metamodel for the Eclipse platform.
The Graphical Editing Framework (GEF)
- The Graphical Editing Framework (GEF) provides a foundation for building rich, interactive user interfaces which are not easily built using native widgets found in the base Eclipse platform.
- GEF has two plug-ins:
- Draw2D : the lightweight toolkit for painting and layout on an SWT Canvas
- GEF : an interactive MVC framework built on top of Draw2d. Draw2d focuses on efficient painting and layout of figures. The GEF plug-in adds editing on top of Draw2d.
The Graphical Modeling Framework (GMF)
- Runtime is an application framework for creating graphical editors using EMF and GEF. It aims to provide a generative bridge between EMF and GEF.
- It is a powerful and widely-used framework for implementing graphical editors for EMF-based modelling languages.
- For e.g UML2 Tools is a set of GMF-based editors for viewing and editing UML models.
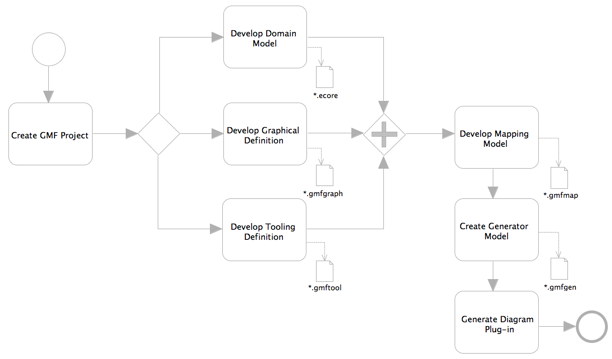
- GMF Tooling Workflow:
Epsilon
- Epsilon is a component of Eclipse that provides infrastructure for implementing uniform and interoperable model management languages.
- It can be used to manage models of diverse metamodels and technologies.
- At the core of Epsilon is the Epsilon Object Language (EOL) which provides features such as model modification, multiple model access, conventional programming
constructs (variables, loops, branches etc.), user interaction, profiling, and support for transactions.
- Although EOL can be used as a general-purpose model management language, its primary aim is to be reused in task-specific languages.
- Thus, a number of task-specific languages have been implemented atop EOL, such as model comparison (ECL) , modelmerging (EML) , model validation (EVL), model refactoring (EWL) and model-to-text transformation (EGL).