Difference between revisions of "Web Application Architectures"
From Suhrid.net Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search (→Rails) |
(→Rails) |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
[[File:Rails-dir-structure.jpg|500px]] | [[File:Rails-dir-structure.jpg|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Philosophy == | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Convention over configuration : Ideally, dev should only specify the unconventional parts of the web-app. | ||
| + | * DRY : Every piece of information should have a single unambiguous authoritative representation within the system. | ||
| + | * Agile Development | ||
Revision as of 02:56, 17 August 2014
Design Patterns
Client - Server Model
- n-tier Architecture : Each tier provides a specific functionality and interacts with adjacent tiers through well defined interfaces.
- Early web-apps were 2-tier client architectures. Server served mainly static web pages.
- 3 Tier Architecture : Most common : Presentation Tier, Application Tier, Data Tier
- App Tier divided into : Business Logic Tier, Data Access Tier (insulates from specific DB)
- Presentation Tier divided into : Client Side UI components, Server Side UI components that generate web pages.
Rails
- Rails is a Ruby gem.
- Uses a lot of code generators, automated testing scripts etc.
- Provides additinal tools such as Rake - to create/migrate databases, clear web session data etc.
- WEBrick is the web server that is bundled with Rails.
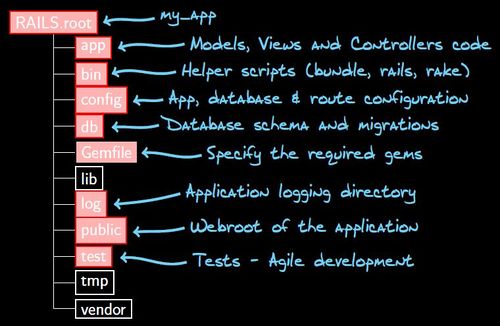
- Rails directory structure :
Philosophy
- Convention over configuration : Ideally, dev should only specify the unconventional parts of the web-app.
- DRY : Every piece of information should have a single unambiguous authoritative representation within the system.
- Agile Development