Web Application Architectures
From Suhrid.net Wiki
Design Patterns
Client - Server Model
- n-tier Architecture : Each tier provides a specific functionality and interacts with adjacent tiers through well defined interfaces.
- Early web-apps were 2-tier client architectures. Server served mainly static web pages.
- 3 Tier Architecture : Most common : Presentation Tier, Application Tier, Data Tier
- App Tier divided into : Business Logic Tier, Data Access Tier (insulates from specific DB)
- Presentation Tier divided into : Client Side UI components, Server Side UI components that generate web pages.
Rails
- Rails is a Ruby gem.
- Uses a lot of code generators, automated testing scripts etc.
- Provides additinal tools such as Rake - to create/migrate databases, clear web session data etc.
- WEBrick is the web server that is bundled with Rails.
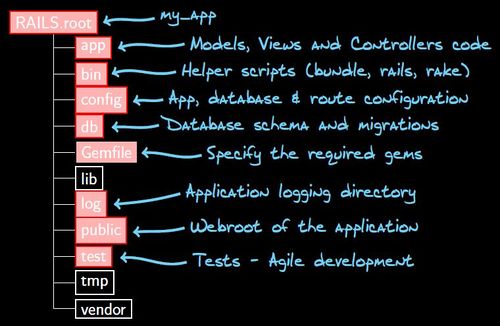
- Rails directory structure :
Philosophy
- Convention over configuration : Ideally, dev should only specify the unconventional parts of the web-app : Models, view, controllers, tests auto created using certain conventions.
- DRY : Every piece of information should have a single unambiguous authoritative representation within the system. e.g, model maps directly to DB column name and is kept in sync if used correctly. Therefore, makes it easy to use code-generators, automatic build systems.
- Agile Development : Emphasizes working software as the primary measure of progress. In dev mode, there are no recompile, deploy, restart cycles. Testing is built into Rails.
- XP is an agile approach that centres around TDD. BDD extends TDD by writing test cases in natural language that non programmers can read. So all stakeholders can be involved easily.